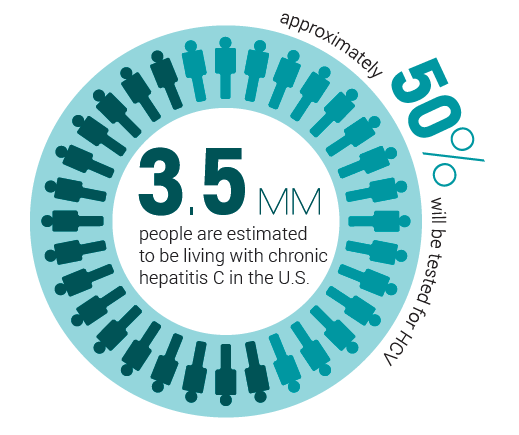
An estimated 3.5 million persons in the United States are infected with HCV, and as many as half of those infected remain undiagnosed. HCV is the primary cause of adult liver transplant candidacy, representing 30 percent of all adults on the transplant waiting list. Baby boomers (those born between 1945 and 1965) account for 75 percent of all chronic HCV infections.
Testing Recommendations
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a virally mediated disease of the liver with a propensity to cause chronic infection, leading to cirrhosis and an increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. Adults born between 1945 and 1965 should be screened for HCV infection; individuals with certain risk behaviors (e.g., injection drug use) or risk exposures (e.g., healthcare workers) should also be screened. Laboratory testing involves screening for HCV antibodies followed by confirmatory RNA testing for positive results.
Laboratory Testing
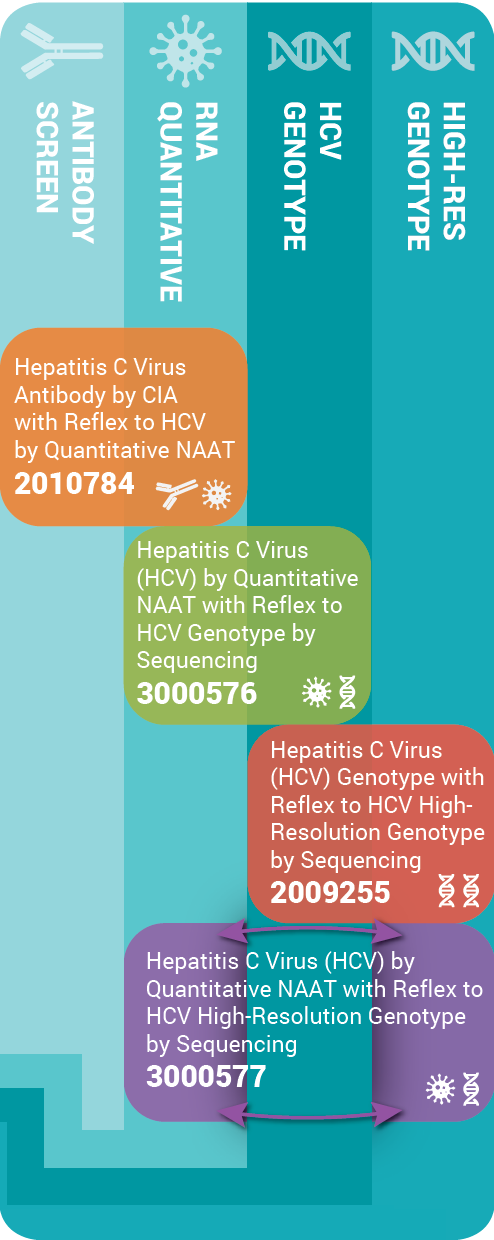
ARUP has designed testing methods that are economical, reduce turnaround time, and help avoid multiple patient draws/visits. Each test can be ordered individually or as part of the reflexive tests to meet our clients’ various testing requirements.
• HCV antibody screen by immunoassay: initial testing for individuals at risk for HCV infection.
• HCV quantification by NAAT if reactive: used to confirm active HCV infection, establish baseline viral load for prognosis, and to monitor response to therapy.
• HCV genotype by sequencing: guide selection of direct acting antiviral (DAA) therapy.
• HCV antibody, with reflex to HCV quantification by NAAT: preferred reflex test for screening and confirming HCV in at-risk individuals. If positive, reflexes to quantitative HCV NAAT to confirm HCV infection.
Chronic Viral Hepatitis and Liver Fibrosis
If left untreated, chronic viral hepatitis can lead to liver fibrosis, the scarring of liver tissue. Staging fibrosis is important for prognosis and monitoring therapy, as the accumulation of fibrosis can lead to cirrhosis and end-stage liver disease. A liver biopsy is considered the gold standard for staging fibrosis but has several limitations. FibroMeter is a blood test used to aid in the evaluation and management of liver fibrosis. This test was specifically designed for patients with chronic viral hepatitis (with or without HIV co-infection). This non-invasive blood analysis is from the creators of the FibroScan instrument.
Visit our Echosens FibroMeter (Liver Fibrosis, Chronic Viral Hepatitis) section for more information.
Additional Resources
- Hepatitis C Virus Trifold Brochure
- Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) by Quantitative NAAT Test Highlight
- Hepatitis C Virus NS5A Test Highlight
- Hepatitis C Virus—HCV
ARUP Consult. - Hepatitis C Information for Health Professionals
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) - Focus on HCV by TMA
Video lecture presented by David R. Hillyard, MD - Spotlight on Testing: Hepatitis C Virus NS5A Drug Resistance by Sequencing
Video lecture presented by David R. Hillyard, MD - Non-invasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis
Video lecture presented by Patricia R. Slev, PhD
For additional information, please call ARUP Client Services at 800-522-2787 and mention keyword: HEPC.